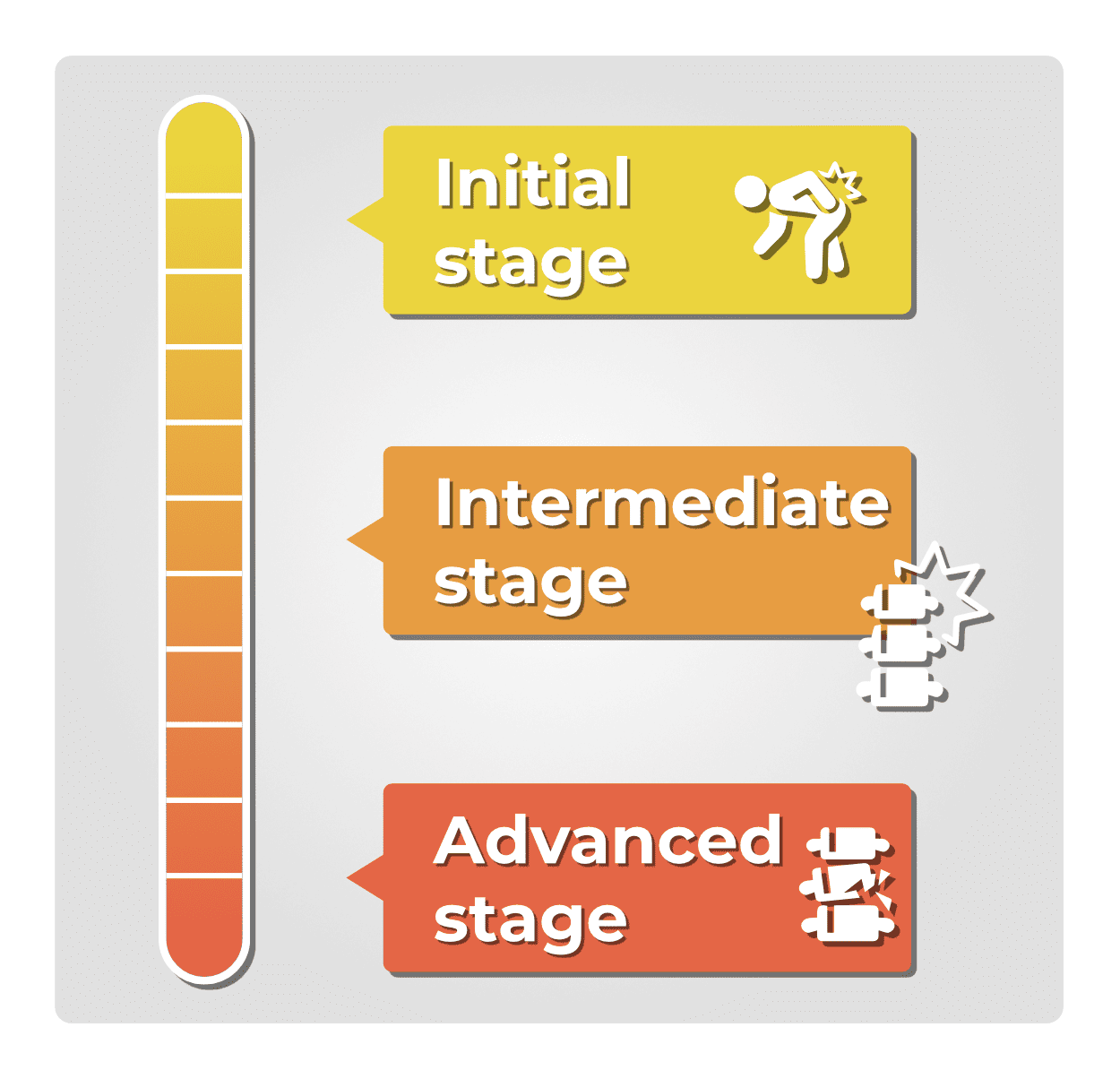
Musculoskeletal disorders present symptoms that evolve according to their location and nature. Their initial manifestation is often subtle, progressing through several distinct stages thereafter.
Musculoskeletal Disorders:
The complete guide
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are diseases of the musculoskeletal system, mainly affecting muscles, tendons, ligaments, nerves, joints and other structures. They result in work-related difficulties and pain.
Since 2023, cases of MSDs have increased by 60% compared with previous years. In 2015, these disorders accounted for over 87% of occupational illnesses resulting in absence or financial compensation due to sequelae. In Europe, average annual growth over the past decade has been 13%.
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are caused by a combination of various risk factors, including:
MSDs typically result from the interaction of biomechanical, psychosocial, individual, organizational, and environmental factors, and are strongly associated with workplace activities.

MSDs mainly affect the upper limbs (shoulders, elbows and wrists), neck, back and lower limbs (knees).
Source : Ameli.fr
Table 57 provides a list of occupational diseases caused by certain work gestures and postures, particularly periarticular affections. These are joint-related disorders caused by repeated or long-term movements and postures. (Based on French occupational disease tables)
Carpal tunnel syndrome refers to disorders caused by compression of the median nerve at the wrist. Symptoms include altered sensitivity, reduced strength and pain in the first three fingers and half of the fourth finger on the thumb side.
Carpal tunnel syndrome is very common, particularly among women between 30 and 50 years old. It can affect one or both hands.
Guyon’s canal syndrome is caused by compression and inflammation of the ulnar nerve as it passes through Guyon’s canal in the wrist. It is characterized by pain in the last two fingers (ring and little fingers), which can extend up to the wrist, elbow and forearm.
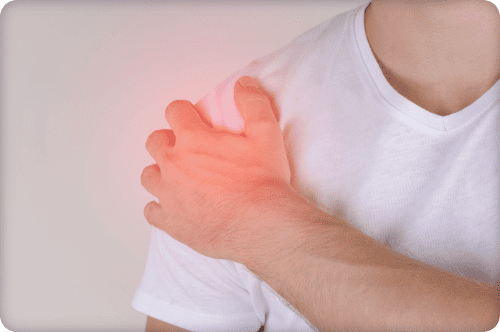
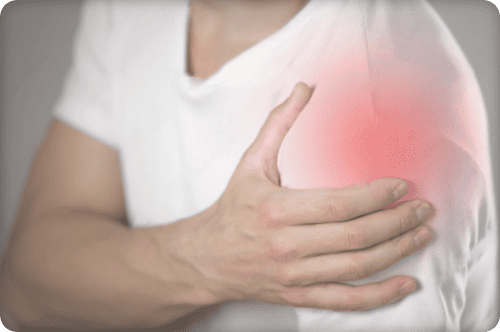
Rotator cuff syndrome is a shoulder disorder characterized by damage to, or irritation of, the tendons and muscles that support and assist movement of the rotator cuff. The rotator cuff is composed of four main muscles (supraspinatus, infraspinatus, lesser tuberosity and subscapularis) and their tendons, which surround the head of the humerus and enable a wide variety of shoulder movements.
or
Epicondylitis is an inflammation of the tendons of the elbow, causing pain around the outside of the elbow due to damage in the tendons of the forearm muscles that are attached to the epicondyle.
Epitrochleitis is an inflammation of the tendons located on the medial or internal edge of the elbow, inserting at the epitrochlea (medial or internal outgrowth of the humerus). Epitrochleitis is the equivalent of epicondylitis, but on the opposite side of the elbow to the little finger.
Low back pain, also known as “lumbago” or “backache”, is pain, often intense, in the lumbar vertebrae at the base of the back. In the case of lumbago, you may also experience a feeling of being unable to move, or difficulty in performing specific movements.
Hygroma of the knee is an inflammation of the bursa located in front of the kneecap. This inflammation leads to an increase in the volume of the bursa, with the appearance of fluid.
Source : Tableau57
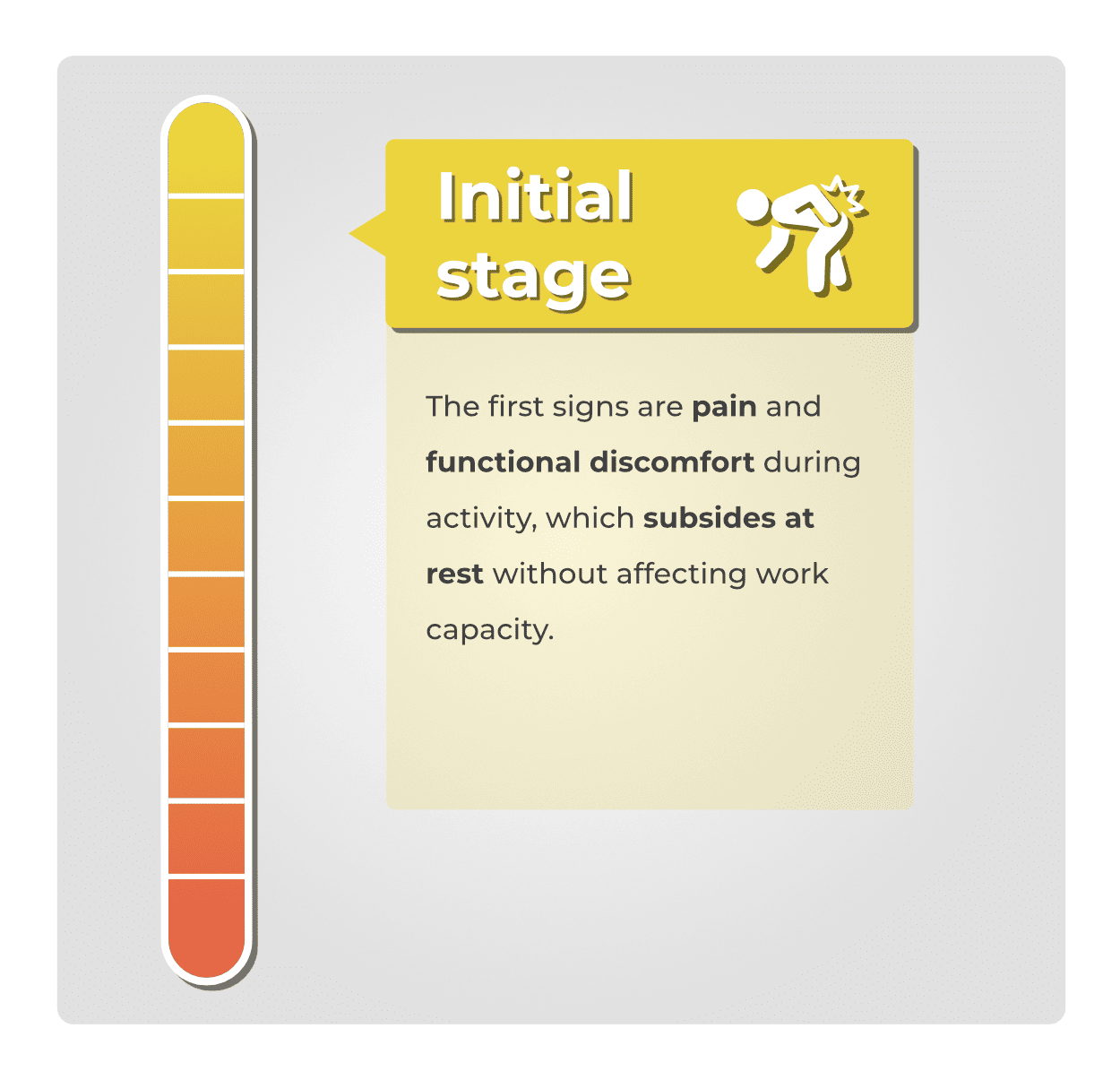
The initial signs are characterized by pain and functional discomfort during activity, which subsides with rest without affecting the ability to work.
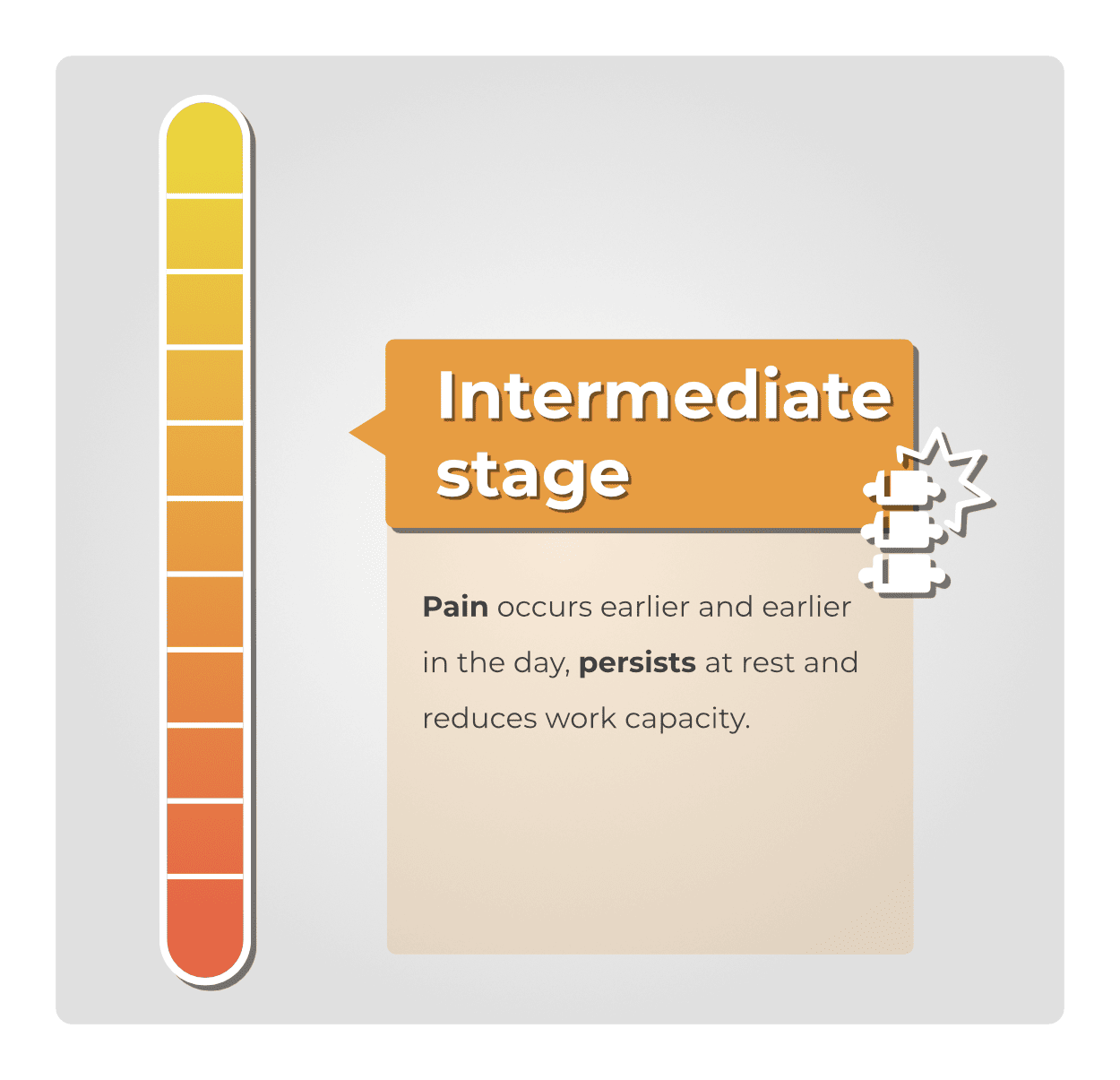
Pain begins to occur earlier in the day, persists during rest, and reduces the ability to work.
Symptoms become more specific, including signs of inflammation, impaired mobility or strength, and even muscle atrophy. These lead to an inability to perform usual work tasks.

Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) have a significant cost for companies. We identify 3 different types of cost:
Direct costs including health insurance contributions, compensation paid to employees absent due to illness, sums spent on adapting workstations and time spent managing and administering the files of affected employees. In 2017, the direct cost to companies amounted to nearly €2 billion.
Indirect costs represent between 2 and 7 times the direct costs, according to Anact, and include the costs of replacing and administrative management, as well as costs linked to organizational dysfunctions and the company’s brand image.
Strategic costs are related to the limitations posed by MSDs. These costs are not calculated in the same way as the previous ones, since they concern personnel (risk of conflict, QWL, etc.), production (more time required to carry out the same task), orders (due to an increase in product prices) or ethics (poor corporate image).
Average cost: €12 780
Duration of work stoppage: 151 days
Average cost: €17 000
Duration of work stoppage: 220 days
Average cost: €52,759
Duration of work stoppage: 298 days

Average cost: €18,220
Duration of work stoppage: 195 days
MSDs account for 87% of occupational diseases.
45% of MSDs result in long-term consequences with significant risks of professional disinsertion.
MSDs account for 20% of reported workplace accidents, according to the latest figures.
The direct cost to businesses is nearly €2 billion annually on average.
MSDs result in 22 million lost workdays.
Musculoskeletal disorders (MSDs) are prevalent across all industries, with no sector being exempt. All sectors must implement measures to address and prevent these disorders.
The most impacted sectors include:

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 95%
Annual contributions paid: €73 million
Lost workdays: 860,000 days
(equivalent to over 4,000 full-time jobs)

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 98%
Annual contributions paid: €113 million
Lost workdays: 1.5 million days
(equivalent to over 7,300 full-time jobs)

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 97%
Annual contributions paid: €77 million
Lost workdays: 930,000 days
(equivalent to over 4,300 full-time jobs)

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 97%
Annual contributions paid: €29 million
Lost workdays: 440,000 days
(equivalent to over 2,000 full-time jobs)

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 91%
Annual contributions paid: €186 million
Lost workdays: 1.8 million days
(equivalent to over 8,500 full-time jobs)

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 79%
55% of workplace accidents in the sector involve manual handling.
Lost workdays: 2.7 million days

Proportion of MSDs among diseases in this sector: 95%
Annual contributions paid: €160 million
Lost workdays: 2.3million days
(equivalent to over 10,000 full-time jobs)
Source : Ameli.fr
The MSD prevention approach is based on three fundamental principles:
1 – A global approach to consider all risk factors.
2 – The involvement of all company stakeholders.
3 – The sharing of knowledge and expertise.
The MSD prevention approach primarily relies on the intervention phase, which includes four key stages:
Understand the stakes.
Set up necessary resources.
Involve different employees.
Identify the risks.
Analyze work situations.
Recognize risk factors.
Reduce work constraints.
Train and inform workers.
Maintain physical capabilities.
Use all the resources from the investigation phase to assess the improvements made.
For every €1 invested by companies, MSD prevention returns €2.18 to the company.
Although costly, MSD prevention proves to be far more economical for companies in the long term. Benefits include increased productivity thanks to improved working conditions, a reduction in occupational illnesses and lower employer health insurance contributions.
Simply use Nawo Live to carry out your ergonomic analyses in a simple and automated way.